Difference between revisions of "Osiris"
Antiyonder (talk | contribs) (→History) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
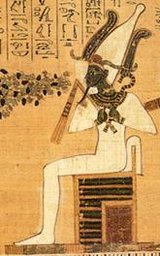
[[Image:osiris.jpg|thumb|160px|Osiris]] | [[Image:osiris.jpg|thumb|160px|Osiris]] | ||
| − | '''Osiris''' is a | + | '''Osiris''' is a deity who was worshiped in Ancient [[Egypt]]. {{CIT|He is considered a death god like [[Anubis]].}} |
| − | + | __TOC__ | |
| + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
==Characteristics== | ==Characteristics== | ||
{{CIT|Osiris is a death god. Whereas Anubis is more a part of the fabric of death (and thus less concerned with being in charge), Osiris became "the boss" by virtue of bringing rank to the table.}} [http://www.s8.org/gargoyles/askgreg/search.php?qid=2982] | {{CIT|Osiris is a death god. Whereas Anubis is more a part of the fabric of death (and thus less concerned with being in charge), Osiris became "the boss" by virtue of bringing rank to the table.}} [http://www.s8.org/gargoyles/askgreg/search.php?qid=2982] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
==Appearances== | ==Appearances== | ||
| − | * | + | * [[Grief|"Grief"]] (Mentioned Only) |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
[[Category:Canon characters]] | [[Category:Canon characters]] | ||
[[Category:Magic]] | [[Category:Magic]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Deities]] | ||
[[Category:Real world characters]] | [[Category:Real world characters]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:26, 3 March 2025
Osiris is a deity who was worshiped in Ancient Egypt. He is considered a death god like Anubis.
Characteristics
Osiris is a death god. Whereas Anubis is more a part of the fabric of death (and thus less concerned with being in charge), Osiris became "the boss" by virtue of bringing rank to the table. [1]
History
In 1995, the Emir used the Scroll of Thoth to bind the jackal god Anubis with a spell that invoked the power of Osiris, Isis and Set.
Appearances
- "Grief" (Mentioned Only)
See also
- Osiris at Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia